What brings you today is 3DP technology. 3DP technology was invented in 1993 by a team of professors at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Emanual Sachs. Based on this technology, Professor Sachs has obtained more than 40 patents in the field of 3D printing and has created a brand new industry. This technology is widely used in ceramic parts, metal molds, medical devices and other fields of electronic products.
3DP molding has also attracted the attention of domestic scholars. Xi'an Jiaotong University, Tianjin University, Tsinghua University, University of Science and Technology of China, Huazhong University of Science and Technology and other domestic universities have conducted in-depth research on the 3DP process and formed their own characteristics in some fields.
1 3DP technology principle
Three Dimensional Printing (3DP), also known as Ink Adhesive Powder Technology, Adhesive Injection Molding, American Society for Testing and Materials Additive Manufacturing Technical Committee (ASTMF42) defines 3DP as Binder Jetting Compound injection). 3DP technology by Emanuel M. of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology Sachs and John S. Haggerty et al. invented the patent application in 1989 and the patent in 1993. In 1995, MIT licensed 3DP technology to Z Corporation for commercial applications. Z Corporation has been launching a series of 3DP printers since 1997 after being licensed by 3DP technology. Later, the company was acquired by 3D Systems and developed into 3D Systems' ColorJet series printers.
The picture below shows a product from Z Corp, which is printed with starch-blended or epoxy resin as a powder material.
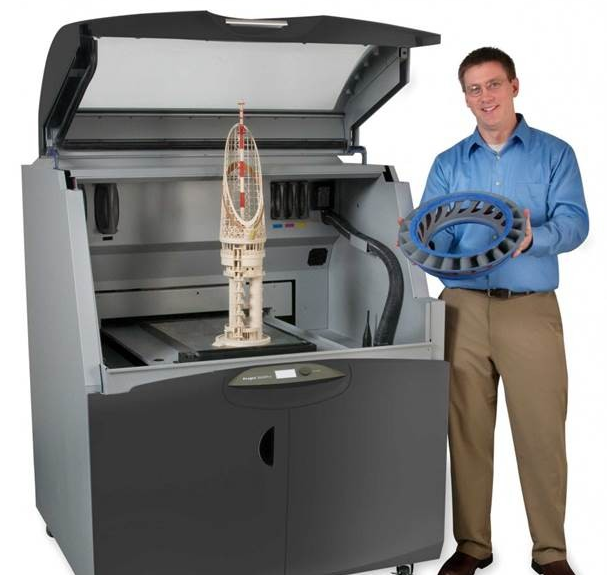

Zcorp Z860
The raw materials used in 3DP printing technology are mainly powder materials such as ceramics, metals, gypsum, plastic powders, etc. Each layer of powder is bonded together using an adhesive and formed by layer stacking. Similar to a normal flat-panel inkjet printer, it is possible to print colored things by bonding powder materials while adding colored pigments. 3DP technology is a relatively mature color 3D printing technology , and other technologies are generally difficult to print in color. Similar to many laser sintering techniques, 3DP also uses a powder bed as the basis, but the difference is that 3DP uses an inkjet printhead to spray the adhesive into the powder instead of using a high energy laser to melt the sintering.

Internal structure of 3DP printer (Source: Antarctic Bear)
Under the control of the control system, the 3DP equipment evenly lays a layer of powder on the platform. The powder-printing head is responsible for the movement of the X-axis and the Y-axis, and moves according to the cross-section data obtained by the model slicing, selectively bonding. The agent is sprayed to finally form a planar pattern. After the completion of the single section pattern, the printing table is lowered by the height of one layer thickness unit, while the spreading roller is subjected to the powder spreading operation, and then the next sectional printing operation is performed again. The powder is fed, powdered and sprayed repeatedly, and the three-dimensional molded part is finally completed.
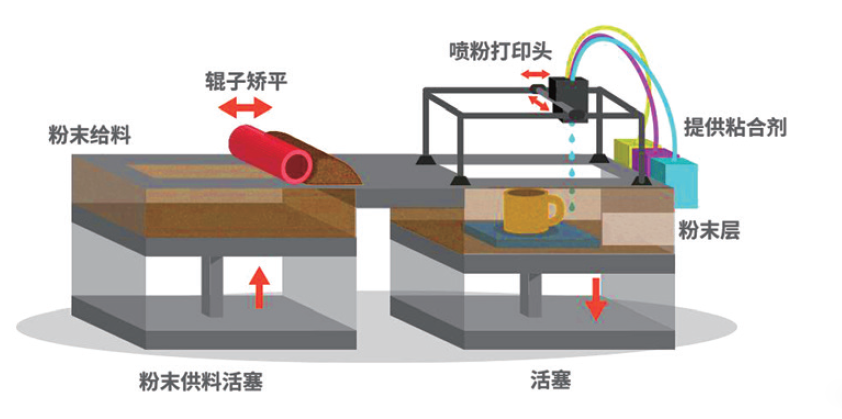
3DP powder bonding molding process (Source: Antarctic Bear)
2 Advantages & Limitations
Nowadays, with many metal laser sintered 3D printers leading the market, 3DP technology has a small market share, but it still plays an important role in the metal additive manufacturing. However, there are often voices questioning whether 3DP technology is still competitive in the case of technologies such as laser sintering. We believe that 3DP technology makes up for some of the shortcomings of other technologies and fills in some gaps in metal 3D printing.
Advantage
1. The 3DP technology is rich in color and has a wide range of materials to choose from. It is a technology with 24-bit full-color printing capability. This is also one of the most competitive features of the technology.
2. Although the 3DP technology has a powder bed but no powder bed melting process, no residual stress is generated during the molding process, so the 3DP can completely support the suspended structure through the powder bed without the need for a support structure (similar to SLS).
3. The 3DP's nozzles can perform 2D array scanning instead of laser spot scanning, so printing speed is fast, enabling printing of large parts.
4. No laser, the equipment is cheaper
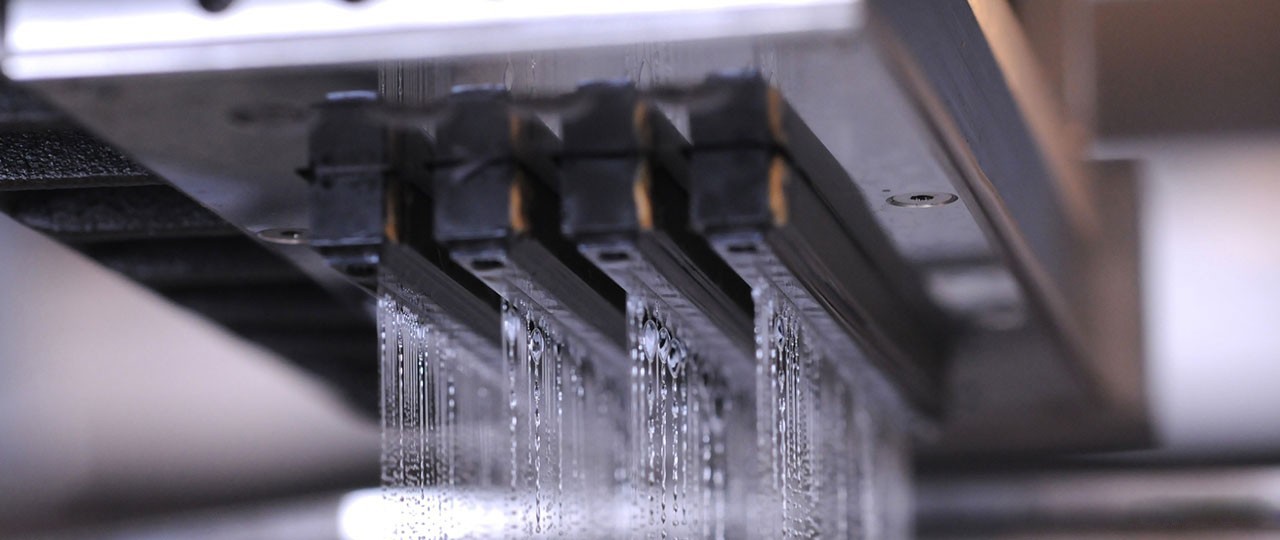

Array nozzle based on 3DP printing technology equipment (Source: ExOne)
A wine rack is a set of shelves for the organized storage of wine. Wine racks can be built out of a number of different materials. The size of the rack and the number of bottles it can hold can vary widely. Wine racks can be located in a winemaker`s professional wine cellar as well as private homes for personal collections.
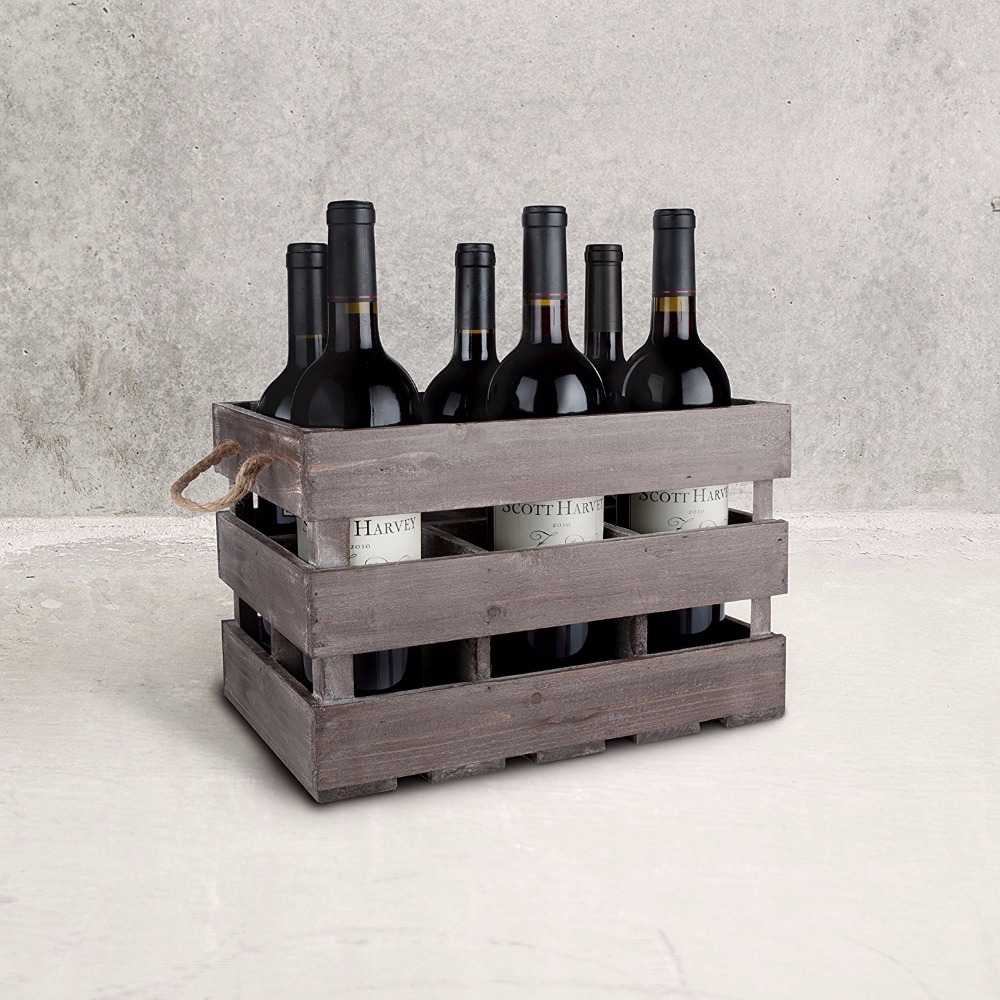

Wood is the most popular medium when it comes to wine rack construction. It is easily obtainable and very workable.
Many types of wood are used. Premium Redwood, All Heart Redwood, Mahogany, Pine, Red Oak, Cedar, and Fir are just a few of the various options. Cedar is popular choice because of the aroma is gives off. This aroma is also its downfall-it can penetrate the wine via the cork. Fir is another popular choice-it also is very strong and comes in a natural cream color.
Wine Rack,Wood Wine Rack,Custom Wine Rack,Wall Mount Wine Rack,Wine Storage Rack
Jinan Tri-Tiger Technology Development Co., Ltd , https://www.tigerwoodproduct.com